Have you ever encountered challenges in photography or videography, such as shallow colors or weak contrast? Or perhaps when photographing nature or water, you faced annoying reflections that hid the true beauty of the scene? In these situations, a polarizing filter (CPL) can be a great solution.
This filter is a highly professional tool specifically designed to tackle reflections, helping you enhance image contrast and make colors significantly more vibrant. Let’s dive into how this filter works, explore its types, and learn why it’s a must-have for photographers and videographers.

- Types of Polarizing Filters (CPL)
Polarizing filters come in two main types:
Circular Polarizer Lens (CPL): These filters are round in shape and screw directly onto the camera lens. The name “CPL” typically refers to this type of filter because it can be rotated to adjust the amount of polarization, making it compatible with autofocus and metering mechanisms in DSLR and mirrorless cameras.
Square or Rectangular Filters: These filters mount on a base or matte box and are mostly used in professional videography. Square filters also provide the same polarizing effect to reduce reflections and enhance contrast, but they are not commonly referred to as CPL due to their shape and mounting system.
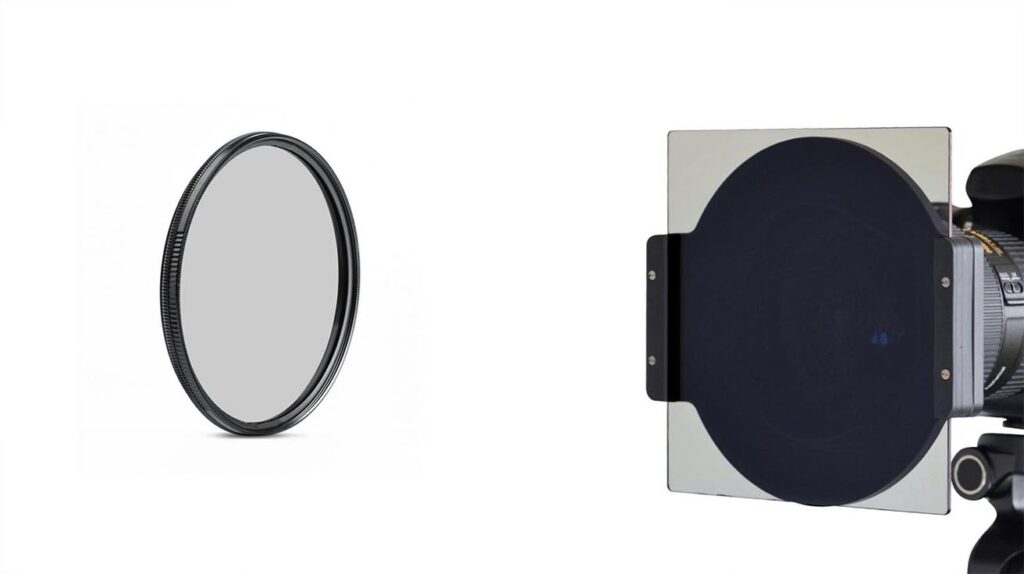

- How a Polarizing Filte1r (CPL) Works
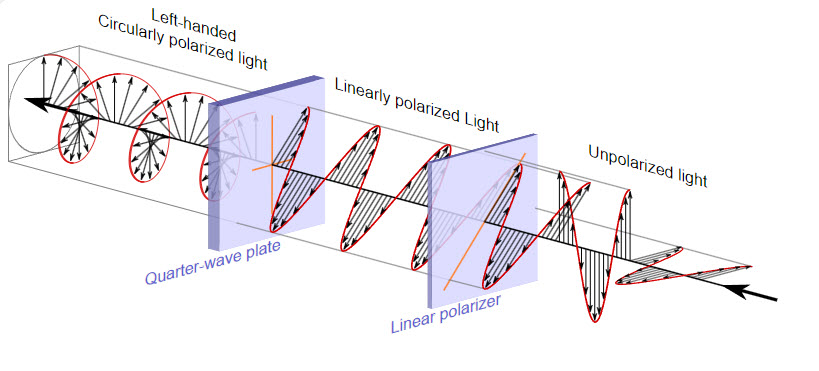
Polarizing filters function by blocking light waves oriented in specific directions. Light naturally reflects off surfaces in multiple directions, but this scattering can reduce image clarity. A polarizing filter only allows light waves oriented in a single direction to pass through, thereby minimizing glare and enhancing contrast.
This unique property makes CPL filters invaluable for controlling how light interacts with your camera sensor. For example, when photographing a lake or a glass building, the filter reduces unwanted reflections, unveiling the true details of the scene.
- Benefits of Using a Polarizing Filter (CPL)
By using a polarizing filter, you can:
Reduce Unwanted Reflections: Reflections on shiny surfaces such as water, glass, or even leaves can hide image details. A CPL filter minimizes these reflections, allowing you to capture more details.
Increase Image Contrast: This filter helps boost contrast and depth of colors. For example, when photographing the sky, it can make the blue color richer and more saturated.
4. Best Situations to Use a Polarizing Filter (CPL)
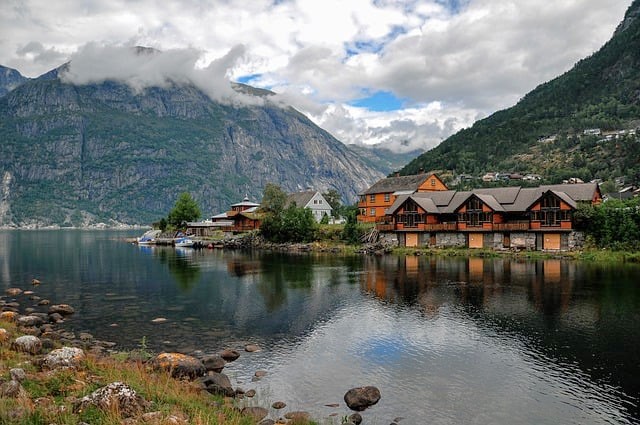
Nature and Landscape Photography: When photographing natural scenes, trees, rivers, lakes, or even forests, this filter helps produce sharper and more natural images.
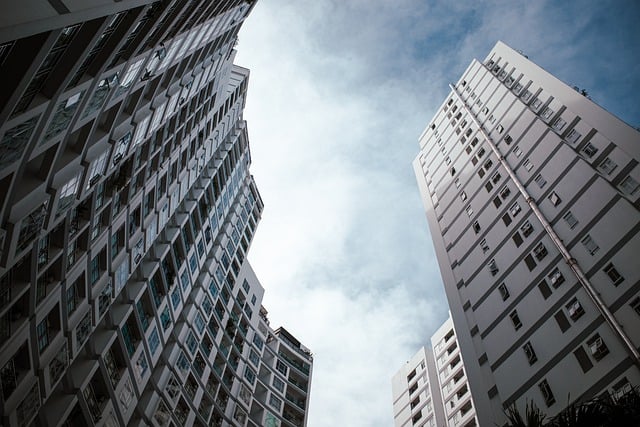
Urban and Architectural Photography: Reflections from windows and metallic surfaces in architectural photography can reduce image clarity. A CPL filter eliminates these reflections and provides a clearer image.


5. Common Mistakes When Using a Polarizing Filter (CPL)
While polarizing filters can enhance your images, improper use can lead to suboptimal results. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Overuse in Low-Light Conditions: Using a polarizing filter in low-light environments can unnecessarily darken your image. It’s better suited for bright daylight settings.
Ignoring Compatibility: Not all lenses are compatible with certain types of filters, especially ultra-wide-angle lenses where vignetting can occur.
Incorrect Angle: Failing to align the filter correctly can result in uneven polarization, leading to dark spots or inconsistent contrast.
6. Choosing the Right Polarizing Filter (CPL)
When selecting a polarizing filter, consider the following factors:
- Lens Diameter: Ensure the filter size matches your lens diameter.
- Coatings: High-quality filters often feature multi-coatings that reduce reflections and improve durability.
- Budget: While cheaper options are available, investing in a reliable brand like Hoya, B+W, or Tiffen ensures better performance and longevity.
7. Advanced Tips for Using Polarizing Filters (CPL)
For photographers and videographers looking to push the boundaries, here are some advanced tips:
- Stacking Filters: Combine a CPL filter with an ND filter to achieve unique effects in long-exposure photography.
- Creative Uses: Use the filter to emphasize reflections selectively, such as capturing vivid skies reflected in water surfaces.
- Testing Angles: Rotate the filter while observing the viewfinder or live view to find the perfect polarization angle.

8. Key Considerations When Using a Polarizing Filter (CPL)
- Light Angle: The filter works best when light strikes the lens at a 90-degree angle. When light hits directly, the effect of the filter is reduced.
- Exposure: Due to the reduction in the amount of light reaching the sensor, keep in mind that a polarizing filter can decrease exposure by up to 2 stops, meaning camera settings may need to be adjusted accordingly.
9. Additional Applications of Polarizing Filters (CPL)
Beyond photography, polarizing filters also play a significant role in cinematography and scientific research. Filmmakers use them to control reflections during outdoor shoots, while scientists employ them in optical experiments and material analysis.
Conclusion
Polarizing filters (CPL) are versatile tools that go beyond reducing reflections. They enhance contrast, enrich colors, and offer creative opportunities to capture stunning visuals. Whether you’re a landscape photographer aiming to capture vivid skies or a filmmaker working on a reflective scene, mastering the use of a polarizing filter can elevate your work to a professional level.
Invest in a good-quality filter, understand how to use it effectively, and take the time to experiment. The results will be breathtaking, helping you achieve vibrant and detailed images that stand out.

